FST(有限状态转换器)是 Elasticsearch 底层的关键数据结构,它通过高效的内存利用和快速检索能力支撑着大规模数据搜索。本文深入分析 FST 原理及其实际应用。
什么是 FST?
FST(Finite State Transducer)是一种高效的数据结构,本质上是一个有向图,用于将输入序列映射到输出值。它具备以下特点:
极高的空间压缩率,通过共享前缀和后缀节约内存
快速的查询速度,支持 O(len(input))时间复杂度的查找
同时支持正向和反向查询
保持输入的词典顺序
FST 数据结构原理
FST 通过构建有向图来存储和查询数据。下面使用图表展示一个简单的 FST 结构:
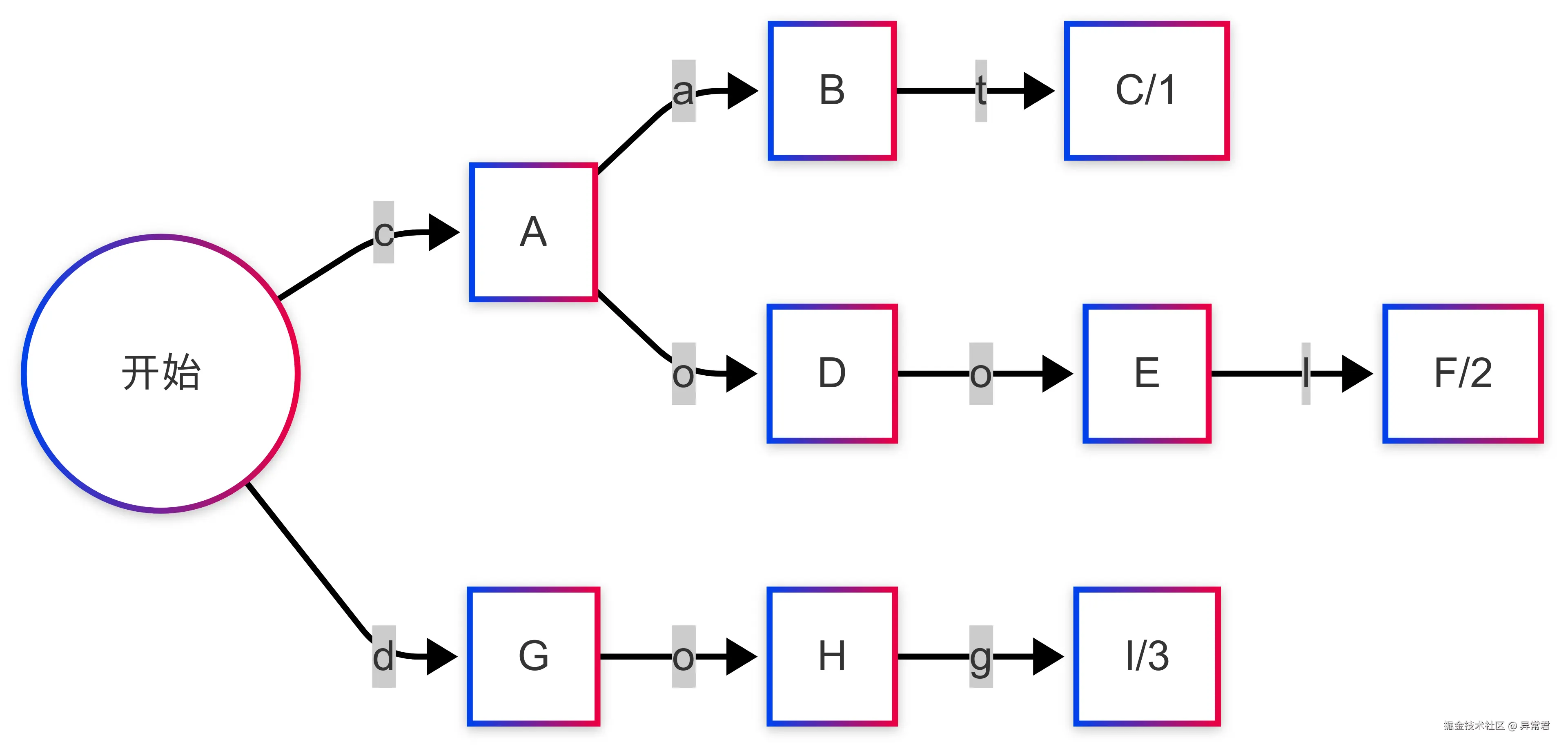
上图 FST 存储了三个映射:"cat"→1, "cool"→2, "dog"→3。注意所有路径如何共享相同的前缀,这正是 FST 节省空间的关键。
FST 内部实现原理
FST 的核心实现基于以下技术:
状态压缩: 每个节点存储为一个紧凑的字节序列
边共享: 相同的转换序列只存储一次
输出关联: 每条路径关联一个输出值
FST 构建过程分为两个阶段:
构建阶段: 按字典序添加输入项,临时保存状态转换
冻结阶段: 完成所有添加后,优化内存布局并冻结结构
// FST构建内部过程示意
void buildFST() {
// 1. 创建初始状态
int startState = builder.createState();
// 2. 添加所有输入(必须有序)
for (InputOutput entry : sortedEntries) {
// 3. 为每个输入创建路径
builder.addPath(startState, entry.input, entry.output);
}
// 4. 冻结并优化FST结构
builder.freeze();
// 5. 此后FST不可修改
}FST 与其他数据结构对比
| 数据结构 | 内存效率 | 查询性能 | 构建成本 | 可修改性 | 适用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HashMap | 低 | O(1) | 低 | 高 | 随机查询频繁 |
| Trie 树 | 中 | O(len) | 中 | 高 | 前缀查询 |
| FST | 高 | O(len) | 高 | 不可修改 | 内存受限环境 |
| B+树 | 中 | O(log n) | 中 | 中 | 范围查询 |
FST 相比 Trie 树的主要优势在于内存效率,通过共享前缀和后缀,FST 可以将相似字符串高度压缩。
但这也带来了一个明显的限制:FST 一旦构建完成就不可修改,这也是为什么 Elasticsearch 需要在索引刷新时重建 FST。
FST 在 Elasticsearch 中的应用场景
1. 词典压缩与管理
Elasticsearch 使用 FST 存储索引中的所有词项(terms)。这是它最核心的应用:
// 适用于Elasticsearch 7.x/Lucene 8.x
public class FSTDictionaryExample {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(FSTDictionaryExample.class);
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建构建器
final PositiveIntOutputs outputs = PositiveIntOutputs.getSingleton();
final FSTCompiler<Long> compiler = new FSTCompiler<>(FST.INPUT_TYPE.BYTE1, outputs);
try {
// 添加映射(必须按字典顺序)
// BytesRef是Lucene用于表示二进制数据的封装类,支持排序和比较
compiler.add(new BytesRef("apple"), 1L);
compiler.add(new BytesRef("apply"), 2L);
compiler.add(new BytesRef("awesome"), 3L);
compiler.add(new BytesRef("ball"), 4L);
// 构建FST
FST<Long> fst = compiler.compile();
// 查找词 - FST查询是线程安全的,可并发访问
Long value = Util.get(fst, new BytesRef("apply"));
logger.info("Value for 'apply': {}", value);
// 前缀查询示例
try (BytesRefFSTEnum<Long> fstEnum = new BytesRefFSTEnum<>(fst)) {
BytesRefFSTEnum.InputOutput<Long> result;
BytesRef prefix = new BytesRef("ap");
logger.info("Terms starting with 'ap':");
while ((result = fstEnum.next()) != null) {
if (!result.input.startsWith(prefix)) {
break;
}
logger.info("{} -> {}", result.input.utf8ToString(), result.output);
}
}
// FST持久化示例
Path path = Paths.get("dictionary.fst");
saveFST(fst, path);
// FST加载示例
FST<Long> loadedFST = loadFST(path);
logger.info("FST loaded successfully: {}", loadedFST != null);
} catch (IOException e) {
logger.error("Error while operating on FST", e);
}
}
/**
* 将FST保存到文件
* @param fst 要保存的FST实例
* @param path 保存路径
* @throws IOException 如果IO操作失败
*/
public static void saveFST(FST<Long> fst, Path path) throws IOException {
try (DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(
new BufferedOutputStream(Files.newOutputStream(path)))) {
fst.save(dos);
logger.info("FST saved to {}", path);
}
}
/**
* 从文件加载FST
* @param path FST文件路径
* @return 加载的FST实例
* @throws IOException 如果IO操作失败
*/
public static FST<Long> loadFST(Path path) throws IOException {
try (DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(
new BufferedInputStream(Files.newInputStream(path)))) {
FST<Long> fst = new FST<>(dis, PositiveIntOutputs.getSingleton());
logger.info("FST loaded from {}", path);
return fst;
}
}
/**
* 估算FST内存占用的辅助方法
* @param termCount 词条数量
* @param avgTermLength 平均词条长度
* @return 估计的内存占用(字节)
*/
public static long estimateFSTMemory(int termCount, double avgTermLength) {
// FST通常能压缩到原始数据的10%-20%
double compressionRatio = 0.15;
return (long)(termCount * avgTermLength * compressionRatio);
}
}2. 自动补全与搜索建议
Elasticsearch 的 completion suggester 基于 FST 实现,支持高效的前缀查询:
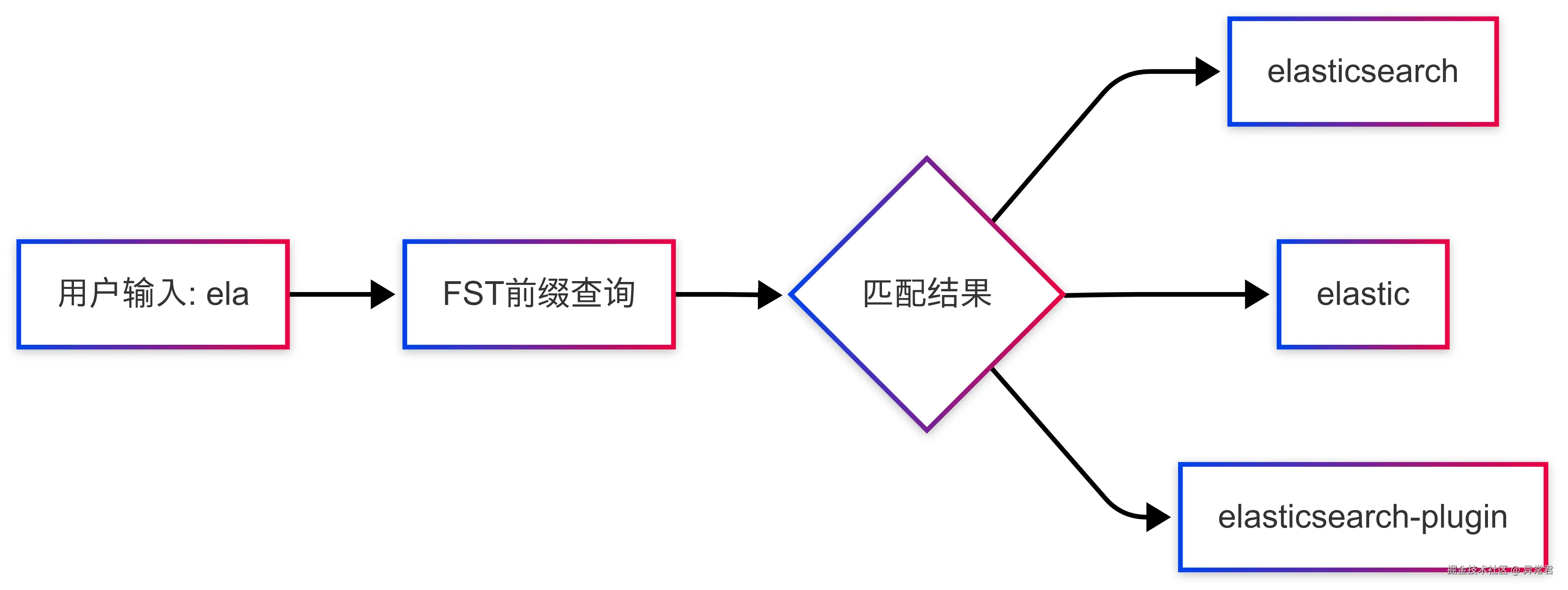
3. 模糊搜索实现
在模糊搜索中,Elasticsearch 使用 FST 结合 Levenshtein 自动机实现高效的模糊匹配:
public class FSTFuzzySearchExample {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(FSTFuzzySearchExample.class);
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建词典
String[] words = {"elastic", "elasticsearch", "engine", "search", "lucene"};
try {
// 检查可用内存,防止OOM
long availableMemory = Runtime.getRuntime().maxMemory() -
(Runtime.getRuntime().totalMemory() - Runtime.getRuntime().freeMemory());
long estimatedMemory = estimateFSTMemory(words.length,
Arrays.stream(words).mapToInt(String::length).average().orElse(0));
if (estimatedMemory > availableMemory * 0.5) {
logger.warn("Warning: FST may consume too much memory. Estimated: {} bytes", estimatedMemory);
}
// 构建FST
final PositiveIntOutputs outputs = PositiveIntOutputs.getSingleton();
final FSTCompiler<Long> compiler = new FSTCompiler<>(FST.INPUT_TYPE.BYTE1, outputs);
// 必须按字典序添加
Arrays.sort(words);
for (int i = 0; i < words.length; i++) {
compiler.add(new BytesRef(words[i]), (long) i);
}
FST<Long> fst = compiler.compile();
// 模糊查询: 允许2个编辑距离
String query = "elasic"; // 拼写错误
int maxEdits = 2;
// 实际的Lucene实现比这更复杂,这里提供一个更接近真实的示例
// 创建查询自动机
Automaton levAutomaton = LevenshteinAutomata.toAutomaton(
new CharacterRunAutomaton(
Operations.toUtf8(
Operations.determinize(
new Levenshtein(query, maxEdits).toAutomaton(),
Operations.DEFAULT_DETERMINIZE_WORK_LIMIT))));
// 使用自动机进行FST匹配
// 注:这是简化版实现,完整实现更复杂
try (BytesRefFSTEnum<Long> fstEnum = new BytesRefFSTEnum<>(fst)) {
BytesRefFSTEnum.InputOutput<Long> match;
logger.info("匹配结果(编辑距离<={})", maxEdits);
while ((match = fstEnum.next()) != null) {
// 检查当前词是否在编辑距离内
if (LevenshteinDistance.editDistance(
match.input.utf8ToString(), query) <= maxEdits) {
logger.info("{}", match.input.utf8ToString());
}
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
logger.error("Error in fuzzy search", e);
} catch (OutOfMemoryError e) {
logger.error("Out of memory while building FST", e);
// 释放资源并建议解决方案
System.gc();
logger.info("Consider using smaller batches or increasing heap size");
}
}
/**
* 估算FST内存占用
* @param termCount 词条数量
* @param avgTermLength 平均词条长度
* @return 估计的内存占用(字节)
*/
public static long estimateFSTMemory(int termCount, double avgTermLength) {
// FST通常能压缩到原始数据的10%-20%
double compressionRatio = 0.15;
return (long)(termCount * avgTermLength * compressionRatio);
}
}注意:上述代码是简化的示例,实际 Elasticsearch 中的模糊搜索实现更为复杂,使用了专门优化的算法。
FST 的局限性与应对策略
使用 FST 时需要注意以下局限性:
一旦构建完成不可修改 - Elasticsearch 通过定期重建索引解决这个问题
必须按字典序添加数据 - 在构建 FST 前必须对数据进行排序
构建成本较高 - 大型 FST 的构建会消耗大量 CPU 资源
内存压力 - 虽然 FST 节省内存,但构建过程中可能需要大量临时内存
应对策略:
合理设置
indices.memory.index_buffer_size参数控制 FST 构建内存对于超大词典,考虑使用分片策略分散压力
利用
refresh_interval参数控制 FST 重建频率预估 FST 内存占用,避免 OOM 风险
/**
* FST内存使用监控工具
*/
public class FSTMemoryMonitor {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(FSTMemoryMonitor.class);
/**
* 检查FST构建内存是否充足
* @param termsCount 词条数量
* @param avgTermLength 平均词条长度
* @return 是否有足够内存
*/
public static boolean hasEnoughMemory(int termsCount, double avgTermLength) {
// 估算FST构建需要的内存(构建过程需要额外内存)
long estimatedFSTSize = estimateFSTMemory(termsCount, avgTermLength);
long estimatedBuildMemory = estimatedFSTSize * 3; // 构建过程约需3倍存储空间
// 获取当前可用内存
Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
long maxMemory = runtime.maxMemory();
long allocatedMemory = runtime.totalMemory();
long freeMemory = runtime.freeMemory();
long availableMemory = maxMemory - allocatedMemory + freeMemory;
// 判断是否有足够内存(留50%余量)
boolean hasEnough = estimatedBuildMemory < availableMemory * 0.5;
logger.info("FST memory estimation: size={} MB, build={} MB, available={} MB, sufficient={}",
estimatedFSTSize / (1024 * 1024),
estimatedBuildMemory / (1024 * 1024),
availableMemory / (1024 * 1024),
hasEnough);
return hasEnough;
}
/**
* 估算FST内存占用
* @param termCount 词条数量
* @param avgTermLength 平均词条长度
* @return 估计的内存占用(字节)
*/
public static long estimateFSTMemory(int termCount, double avgTermLength) {
// FST通常能压缩到原始数据的10%-20%
double compressionRatio = 0.15;
return (long)(termCount * avgTermLength * compressionRatio);
}
}实战:使用 FST 优化自定义分析器
下面展示如何使用 FST 优化自定义分析器的性能:
public class FSTBasedAnalyzer extends Analyzer {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(FSTBasedAnalyzer.class);
private final FST<CharsRef> synonymFST;
/**
* 使用FST实现高性能同义词分析器
* @param synonymMap 同义词映射表
* @throws IOException 如果FST构建失败
*/
public FSTBasedAnalyzer(Map<String, String> synonymMap) throws IOException {
// 构建同义词FST
FSTCompiler<CharsRef> fstCompiler = new FSTCompiler<>(
FST.INPUT_TYPE.BYTE1,
new CharSequenceOutputs());
// 按字典序添加映射
List<Map.Entry<String, String>> sortedEntries = new ArrayList<>(synonymMap.entrySet());
sortedEntries.sort(Map.Entry.comparingByKey());
// 检查内存
if (!FSTMemoryMonitor.hasEnoughMemory(sortedEntries.size(),
sortedEntries.stream()
.mapToInt(e -> e.getKey().length() + e.getValue().length())
.average().orElse(0))) {
throw new IOException("Not enough memory to build synonym FST");
}
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : sortedEntries) {
fstCompiler.add(new BytesRef(entry.getKey()), new CharsRef(entry.getValue()));
}
this.synonymFST = fstCompiler.compile();
logger.info("FST synonym dictionary built with {} entries", synonymMap.size());
}
@Override
protected TokenStreamComponents createComponents(String fieldName) {
Tokenizer tokenizer = new StandardTokenizer();
TokenStream stream = new FSTSynonymFilter(tokenizer, synonymFST);
return new TokenStreamComponents(tokenizer, stream);
}
/**
* 自定义TokenFilter实现,使用FST进行同义词替换
* CharsRef是Lucene用于字符序列的包装类,支持高效操作
*/
private static class FSTSynonymFilter extends TokenFilter {
private final FST<CharsRef> synonymFST;
private final CharTermAttribute termAttr;
FSTSynonymFilter(TokenStream input, FST<CharsRef> synonymFST) {
super(input);
this.synonymFST = synonymFST;
this.termAttr = addAttribute(CharTermAttribute.class);
}
@Override
public boolean incrementToken() throws IOException {
if (!input.incrementToken()) {
return false;
}
// 查找同义词
BytesRef term = new BytesRef(termAttr.toString());
CharsRef synonym = Util.get(synonymFST, term);
if (synonym != null) {
termAttr.setEmpty().append(synonym);
}
return true;
}
}
}性能测试与优化
在性能测试中,应使用专业的基准测试工具(如 JMH)而非简单的时间测量:
@BenchmarkMode(Mode.AverageTime)
@OutputTimeUnit(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)
@State(Scope.Benchmark)
@Fork(value = 2, jvmArgs = {"-Xms2G", "-Xmx2G"})
@Warmup(iterations = 3)
@Measurement(iterations = 5)
public class FSTBenchmark {
private List<String> terms;
private Set<String> hashSet;
private FST<Long> fst;
@Setup
public void setup() throws IOException {
// 准备测试数据
terms = new ArrayList<>(1_000_000);
for (int i = 0; i < 1_000_000; i++) {
terms.add("term" + i);
}
// 创建HashSet
hashSet = new HashSet<>(terms);
// 创建FST
List<String> sortedTerms = new ArrayList<>(terms);
Collections.sort(sortedTerms);
PositiveIntOutputs outputs = PositiveIntOutputs.getSingleton();
FSTCompiler<Long> compiler = new FSTCompiler<>(FST.INPUT_TYPE.BYTE1, outputs);
for (int i = 0; i < sortedTerms.size(); i++) {
compiler.add(new BytesRef(sortedTerms.get(i)), (long) i);
}
fst = compiler.compile();
}
@Benchmark
public boolean hashSetLookup() {
// 随机查找1000个词
boolean result = false;
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
int idx = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(terms.size());
result |= hashSet.contains(terms.get(idx));
}
return result;
}
@Benchmark
public boolean fstLookup() throws IOException {
// 随机查找1000个词
boolean result = false;
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
int idx = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(terms.size());
result |= Util.get(fst, new BytesRef(terms.get(idx))) != null;
}
return result;
}
@Benchmark
public List<String> prefixLookup() throws IOException {
// 前缀查询
String prefix = "term10";
BytesRef prefixBytes = new BytesRef(prefix);
List<String> results = new ArrayList<>();
try (BytesRefFSTEnum<Long> fstEnum = new BytesRefFSTEnum<>(fst)) {
BytesRefFSTEnum.InputOutput<Long> result;
while ((result = fstEnum.next()) != null) {
if (!result.input.startsWith(prefixBytes)) {
break;
}
results.add(result.input.utf8ToString());
if (results.size() >= 100) break; // 限制结果数量
}
}
return results;
}
}Elasticsearch 中的 FST 配置参数
在 Elasticsearch 中,以下参数会影响 FST 的性能和内存使用:
indices.memory.index_buffer_size
控制索引缓冲区大小,影响 FST 构建内存
默认为堆内存的 10%
建议:大型索引可适当增加
indices.queries.cache.size
影响术语查询缓存,可减轻 FST 查询压力
默认为堆内存的 1%
建议:高查询负载时增加
refresh_interval
控制索引刷新频率,影响 FST 重建频率
默认为 1 秒
建议:批量导入时可增大,减少 FST 重建频率
配置示例:
# elasticsearch.yml indices.memory.index_buffer_size: 20% indices.queries.cache.size: 3%索引级配置:
PUT /my_index/_settings
{
"refresh_interval": "30s"
}FST 性能调优决策流程
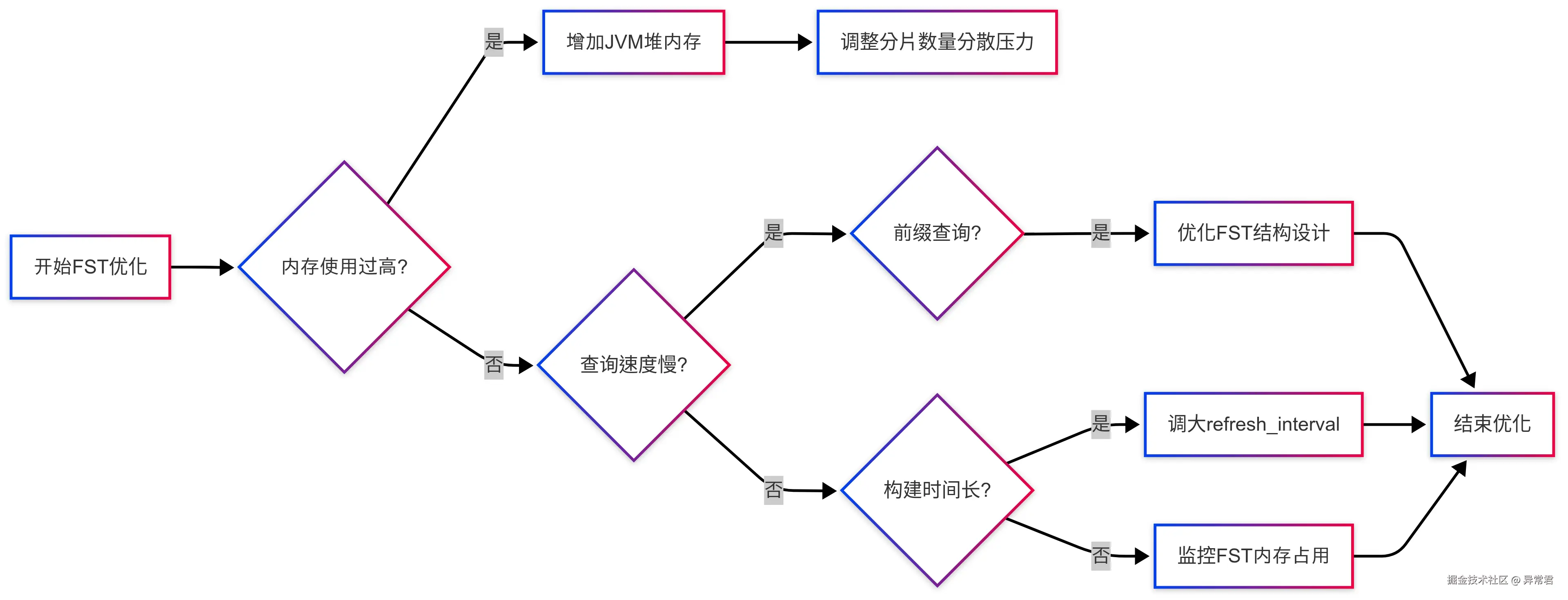
FST 在生产环境中的优化策略
1.内存管理
监控 FST 内存使用率:GET /_nodes/stats/indices/segments
设置合理的 JVM 堆大小,一般不超过物理内存的 50%
启用 G1GC 垃圾收集器处理大型 FST
定期监控和预警 FST 内存占用
2.分片策略
对于超大词典,合理分片可分散 FST 构建压力
避免单节点承载过多主分片
使用索引生命周期管理(ILM)自动管理索引大小
3.预热策略
使用索引预热 API 确保 FST 加载到内存
POST /my_index/_war
4.升级考量
Elasticsearch 7.x 后 FST 性能大幅提升
考虑升级到新版本获取优化
常见问题排查
| 问题现象 | 可能原因 | 解决方法 |
|---|---|---|
| OOM 错误 | FST 构建内存不足 | 增加堆内存或减少批量索引大小 |
| 查询延迟高 | FST 冷启动 | 使用索引预热 API 预加载 FST |
| CPU 使用率高 | FST 频繁重建 | 调整 refresh_interval 减少重建频率 |
| 索引速度慢 | FST 构建阻塞 | 增加索引缓冲区大小,调整分片 |
| 内存使用持续增长 | FST 碎片化 | 定期合并索引,优化内存使用 |
总结
| 应用场景 | 优化效果 | 实现难点 | 注意事项 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 词典存储 | 内存减少 80-90% | 需要有序输入 | 构建过程 CPU 密集 |
| 前缀查询 | 查询时间 O(len) | 自定义 FST 结构设计 | 需预热避免冷启动慢 |
| 模糊搜索 | 比暴力匹配快 10 倍+ | Levenshtein 自动机结合 | 编辑距离越大性能越差 |
| 自动补全 | 响应时间<10ms | 权重整合 | 需定期重建更新 |
| 同义词扩展 | CPU 使用降低 30% | 输出映射设计 | 无法动态更新 |










